
ORIF often takes place as an emergency or urgent procedure. How do I prepare for a tibia/fibula fracture open reduction and internal fixation? Ask your healthcare provider about the risks that most apply to you. For example, people with low bone mass or diabetes may be at greater risk of some complications. Your own risk of complications may vary according to your age, the anatomy of your fracture, and your other medical conditions. There is also the risk that the fracture won’t heal properly, and you’ll need repeat surgery.
#TIBIA FRACTURE SKIN#

In a “closed reduction,” a healthcare provider physically moves the bones back into place without surgically exposing the bone. During an “open reduction,” orthopedic surgeons reposition your bone pieces during surgery to put them back into their proper alignment.
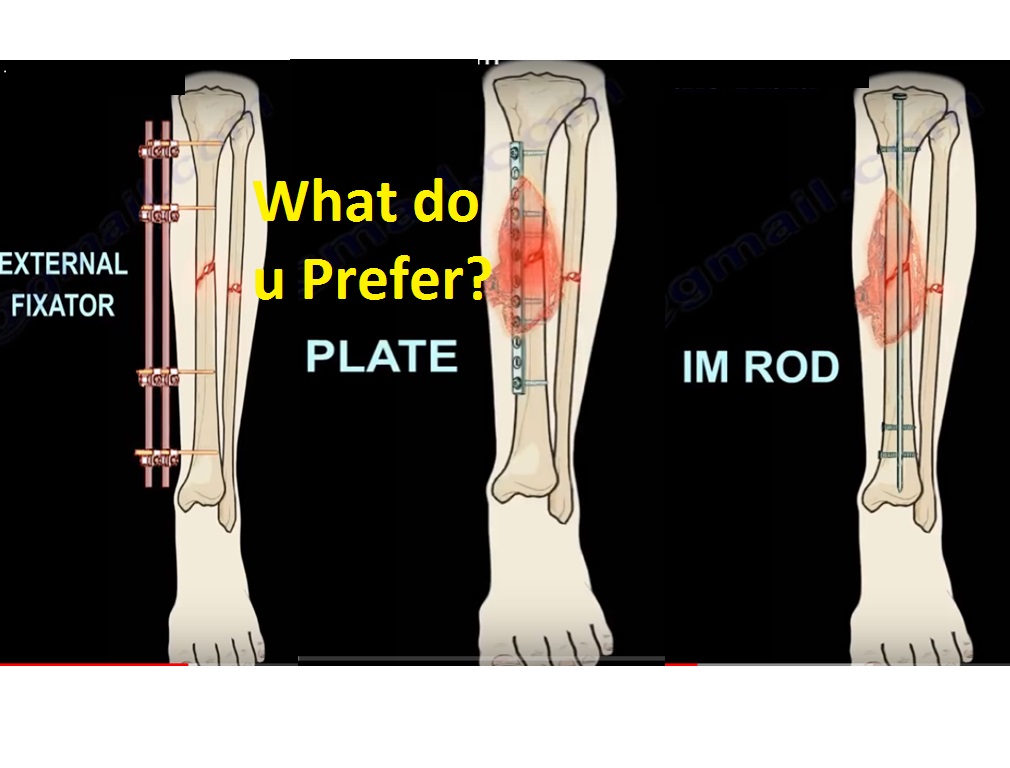
If you fracture your tibia or fibula, you might need ORIF to bring your bones back into place and help them heal.

In other types of fractures, the injury moves the bone fragments out of alignment. In certain types of fractures, your bone breaks, but its pieces still line up correctly. (A fracture here might be called a “broken ankle.”) Only one of these bones might break, or you might have a fracture in both bones. This might happen in the part of the bone near the knee, near the middle long part of the bone, or in the bone near part of the ankle. The ends of the tibia and the fibula both form part of the ankle joint.ĭifferent kinds of injury can damage the tibia or the fibula, causing them to break into one or more pieces. Beside it, more toward the outside of the leg, is the fibula. The tibia, or shin bone, is the larger bone in your lower leg. You might need this procedure to treat your broken shin bone (tibia) or your fibula. Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a type of surgery used to stabilize and heal a broken bone. What is tibia/fibula fracture open reduction and internal fixation?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
